879
Short circuit calculations reference data
The information below was taken from several sources including Square D "Procedure for determining short circuit values in secondary electrical distribution systes" by Russell Ohlson. The values below can be easily revised to any values that the user desires.
Primary Substation Impedance Data
If specific information is not available use the following as a guide. For transformers 501 to 10000kVA 3 phase and 501 to 5000kVA 1 phase. From American Standards Association Standard C57.12.10-1958
(Included in NEMA Transformer Standard TR-1-1962)
| Transformer High Voltage, V | Transformer Low Voltage | |
| 2400V and above | 480V* | |
| 2400 to 22900 | 5.50% | 5.75% |
| 26400 to 34400 | 6% | 6.25% |
| 43800 | 6.50% | 6.75% |
| 67000 | 7% | |
* - generally pertains to all voltages 600V and below
Secondary Substation Impedance Data
High Voltage 15kV Max, Low Voltage 600V Max. If specific information is not available use the following as a guide.
| KVA, 3phase | NEMA Std., % Imp. | General Range of Mfgrs. % Imp. | Suggested X/R Ratio for S.C. Calcs | Suggested % Imp. |
| 112.5 | 2 Min. | 2.3 - 5.2 | 5 | 3 Min |
| 150 | 2 Min. | 2.7 - 5.1 | 5 | 3.5 Min |
| 225 | 2 Min. | 4.4 - 5.0 | 5.5 | 4.5 Min |
| 300 | 4.5 Min. | 4.5 - 6.0 | 6 | 4.5 Min |
| 400 | Not Listed | 4.5 - 6.0 | 6 | 4.5 Min |
| 500 | 4.5 Min. | 4.5 - 6.0 | 6 | 5 Min |
| 750 | 5.75 | 5.75 | 7 | 5.75 |
| 1000 | 5.75 | 5.75 | 8 | 5.75 |
| 1500 | 5.75 | 5.75 | 9 | 5.75 |
| 2000 | 5.75 | 5.75 | 12 | 5.75 |
| 2500 | 5.75 | 5.75 | 12 | 5.75 |
Note: NEMA industry standards allow a maximum manufacturing tolerance of +/- 7.5% of the specified transformer impedance value. However, any tolerance is usually ignored in short circuit calculations on the assumption that plus tolerance offers an extra margin of safety and minus tolerance is adequately compensated for by miscellaneous circuit impedances not specifically included in the calculations. But if desired, multiplying the specified impedance, reactance and resistance values by 0.925 will compensate for even the most adverse tolerance conditions.
Click for more transformer impedance and X/R data.
Copper Conductor Cable Reactance and Resistance Data
Typical Values - Use Exact data if Available. Line-To-Neutral mOhm per 100 feet.
| Conductor Size AWG or MCM | Three-Single Conductor Cables | One Three Conductor Cable | ||||||
| In Magnetic Duct | Not In Magnetic Duct | In Magnetic Duct | Not In Magnetic Duct | |||||
| Reactance "X" | Resistance "R" | React "X" | Resist "R" | React "X" | Resist "R" | React "X" | Resist "R" | |
| 14 Solid | 7.51 | 258 | 5.94 | 258 | 5.15 | 258 | 4.48 | 258 |
| 12 Solid | 6.96 | 161 | 5.51 | 161 | 5.02 | 161 | 4.36 | 161 |
| 10 Solid | 6.74 | 101 | 5.34 | 101 | 4.93 | 101 | 4.29 | 101 |
| 8 | 5.93 | 67.9 | 4.74 | 67.9 | 4.54 | 67.9 | 3.95 | 67.9 |
| 8 Solid | 6.06 | 65.9 | 4.85 | 65.9 | 4.64 | 65.9 | 4.04 | 65.9 |
| 6 | 5.67 | 42.7 | 4.54 | 42.7 | 4.34 | 42.7 | 3.78 | 42.7 |
| 6 Solid | 5.88 | 41.5 | 4.7 | 41.5 | 4.5 | 41.5 | 3.92 | 41.5 |
| 4 | 5.3 | 26.9 | 4.24 | 26.9 | 4.06 | 26.9 | 3.53 | 26.9 |
| 4 Solid | 5.55 | 26.1 | 4.44 | 26.1 | 4.25 | 26.1 | 3.7 | 26.1 |
| 2 | 4.98 | 17 | 3.98 | 16.9 | 3.81 | 17 | 3.32 | 16.9 |
| 1 | 5.04 | 13.5 | 4.03 | 13.4 | 3.86 | 13.5 | 3.36 | 13.4 |
| 1/0 | 4.95 | 10.8 | 3.96 | 10.7 | 3.79 | 10.8 | 3.3 | 10.7 |
| 2/0 | 4.83 | 8.6 | 3.86 | 8.5 | 3.7 | 8.6 | 3.22 | 8.5 |
| 3/0 | 4.67 | 6.9 | 3.73 | 6.7 | 3.57 | 6.9 | 3.11 | 6.7 |
| 4/0 | 4.53 | 5.43 | 3.62 | 5.33 | 3.47 | 5.43 | 3.02 | 5.33 |
| 250 | 4.65 | 4.72 | 3.72 | 4.59 | 3.56 | 4.72 | 3.1 | 4.59 |
| 300 | 4.52 | 3.95 | 3.61 | 3.8 | 3.45 | 3.95 | 3.01 | 3.8 |
| 350 | 4.44 | 3.42 | 3.55 | 3.23 | 3.37 | 3.42 | 2.96 | 3.23 |
| 400 | 4.41 | 3.05 | 3.53 | 2.91 | 3.33 | 3.05 | 2.94 | 2.91 |
| 500 | 4.32 | 2.5 | 3.46 | 2.35 | 3.23 | 2.5 | 2.88 | 2.35 |
| 600 | 4.31 | 2.16 | 3.44 | 1.99 | 3.19 | 2.16 | 2.87 | 1.99 |
| 750 | 4.25 | 1.81 | 3.4 | 1.63 | 3.1 | 1.81 | 2.83 | 1.63 |
| 1000 | 4.19 | 1.53 | 3.35 | 1.35 | ||||
Aluminum Conductor Cable Reactance and Resistance Data
Typical Values - Use Exact data if Available. Line-To-Neutral mOhm per 100 feet.
| Conductor Size AWG or MCM | Three-Single Conductor Cables | One Three Conductor Cable | ||||||
| In Magnetic Duct | Not In Magnetic Duct | In Magnetic Duct | Not In Magnetic Duct | |||||
| Reactance "X" | Resistance "R" | React "X" | Resist "R" | React "X" | Resist "R" | React "X" | Resist "R" | |
| 8 | 3.94 | 129.11 | 3.43 | 129.11 | 5.14 | 129.11 | 4.11 | 129.11 |
| 6 | 3.99 | 81.24 | 3.47 | 81.24 | 5.21 | 81.24 | 4.17 | 81.24 |
| 4 | 3.77 | 51.07 | 3.28 | 51.07 | 4.92 | 51.07 | 3.93 | 51.07 |
| 2 | 3.67 | 40.51 | 3.19 | 40.51 | 4.79 | 40.51 | 3.83 | 40.51 |
| 3 | 3.57 | 32.12 | 3.11 | 32.12 | 4.66 | 32.12 | 3.73 | 32.12 |
| 1 | 3.71 | 25.47 | 3.20 | 25.47 | 4.85 | 25.47 | 3.88 | 25.47 |
| 1/0 | 3.50 | 20.19 | 3.05 | 20.19 | 4.57 | 20.19 | 3.66 | 20.19 |
| 2/0 | 3.41 | 16.02 | 2.97 | 16.02 | 4.46 | 16.02 | 3.56 | 16.02 |
| 3/0 | 3.33 | 12.70 | 2.90 | 12.70 | 4.35 | 12.70 | 3.48 | 12.70 |
| 4/0 | 3.26 | 10.07 | 2.83 | 10.07 | 4.25 | 10.07 | 3.40 | 10.07 |
| 250 | 3.28 | 8.68 | 2.85 | 8.54 | 4.28 | 8.68 | 3.42 | 8.54 |
| 300 | 3.20 | 7.27 | 2.80 | 7.13 | 4.20 | 7.27 | 3.36 | 7.13 |
| 350 | 3.15 | 6.27 | 2.76 | 6.12 | 4.14 | 6.27 | 3.31 | 6.12 |
| 400 | 3.11 | 5.53 | 2.73 | 5.36 | 4.09 | 5.53 | 3.27 | 5.36 |
| 500 | 3.01 | 4.51 | 2.68 | 4.29 | 4.02 | 4.51 | 3.21 | 4.29 |
| 600 | 2.99 | 3.84 | 2.69 | 3.58 | 4.04 | 3.84 | 3.23 | 3.58 |
| 750 | 2.88 | 3.18 | 2.64 | 2.88 | 3.96 | 3.18 | 3.17 | 2.88 |
| 1000 | 2.76 | 2.54 | 2.59 | 2.19 | 3.88 | 2.54 | 3.10 | 2.19 |
| 1250 | 2.71 | 2.15 | 2.58 | 1.78 | 3.88 | 2.15 | 3.10 | 1.78 |
| 1500 | 2.65 | 1.89 | 2.55 | 1.51 | 3.83 | 1.89 | 3.06 | 1.51 |
| 1750 | 2.60 | 1.71 | 2.52 | 1.32 | 3.78 | 1.71 | 3.02 | 1.32 |
| 2000 | 2.57 | 1.57 | 2.50 | 1.18 | 3.75 | 1.57 | 3.00 | 1.18 |
Square D Bus Duct Reactance and Resistance Data
| Duct Current Rating, A | Square D Feeder Duct | Square D Plug-In Duct | ||||||
| Aluminum | Copper | Aluminum | Copper | |||||
| Reactance "X" | Resistance "R" | React "X" | Resist "R" | React "X" | Resist "R" | React "X" | Resist "R" | |
| 225 | 6.88 | 6.756 | 6.96 | 7.544 | ||||
| 400 | 6.95 | 3.797 | 7.2 | 2.464 | ||||
| 600 | 0.243 | 1.93 | 3.87 | 2.221 | 7.35 | 1.718 | ||
| 800 | 0.243 | 1.93 | 0.568 | 1.466 | 2.82 | 1.291 | 4.39 | 1.425 |
| 1000 | 0.468 | 1.52 | 0.243 | 1.215 | 2.8 | 1.081 | 4.58 | 0.914 |
| 1350 | 0.516 | 0.99 | 0.595 | 0.847 | ||||
| 1600 | 0.094 | 0.87 | 0.618 | 0.571 | ||||
| 2000 | 0.26 | 0.64 | 0.12 | 0.603 | ||||
| 2500 | 0.147 | 0.514 | 0.3 | 0.415 | ||||
| 3000 | 0.212 | 0.436 | 0.315 | 0.282 | ||||
| 4000 | 0.184 | 0.31 | 0.212 | 0.184 | ||||
Motors and Generators
Motors are a source of short-circuit current. They will act like generators when a short-circuit occurs. At a minimum, motors must be specified by horsepower which will be listed on the motor nameplate. Motor specifications are as follows:
kV: Motor rated kV.
HP: Motor horsepower. Motors may be represented individually or as a lumped group.
FLA: The Full Load Amps.
PF: Motor operating power factor. This is used with the Efficiency to determine kVA. Motor groups should use an average value of power factor.
EFF: Motor operating efficiency. This is used with the Power Factor field to determine kVA. Motor groups should use an average value of efficiency.
kVA/HP: The motor or motor group kVA rating per horsepower. This is a simple way of defining the kVA when full load amperes, or efficiency and power factor are not known. Typical values for standard efficiency motors are listed below:
0.95 kVA/HP - Induction 100 < 999 HP
0.90 kVA/HP - Induction > 1000 HP
0.8 kVA/HP - Synchronous 1.0 PF
Motor FLA Calculations
There are three ways to calculate motor Full Load Ampere (FLA) rating. The FLA calculation methods are shown below in priority order:
If the kVA is known, the motor FLA should be determined by the following equation:
If the motor KVA is not available but motor HP and (kVA/HP) values are known, the motor FLA should be determined from the following equation:
If both the KVA and the (kVA/HP) are not available, the motor FLA should be determined from the following equation:
Motor Impedance and X/R Ratio for Short Circuit Analysis
Reactance to resistance ratio X/R and impedance for short circuit analysis %Z can be read off from the motor nameplate. If motor X/R and/or %Z is not specified on the nameplate, the motor manufacturer may be able to supply this. When contacting the motor manufacturer, it may be helpful to have the motor serial number. Table below displays ANSI Standard impedances and interrupting duty multipliers. Code numbers are chosen according to the motor types, sizes and modeling method. Using the ANSI Code is the recommended method to determine motor impedances used for ANSI Standard short circuit calculations:
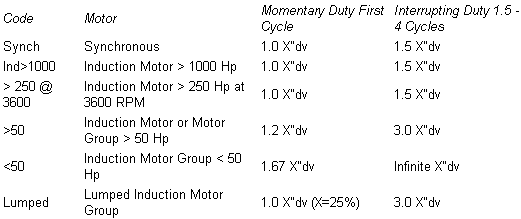
Note: X" for induction motor groups >50 HP and <50 HP are typically assumed equal to 16.7%. Using the impedance multipliers, this corresponds to an equivalent motor contribution of 3.6 to 4.8 times the full load current.
X/R: The reactance to resistance ratio from the motor nameplate or manufacturer spec sheet [typical data].
X"dv: Subtransient reactance in percent on the motor HP base. Normally this is 16.7% for induction motors. Average subtransient reactances for three phase synchronous machines are:
0.2 for salient pole generators and motors
0.24 for air cooled condensers
Software & Mobile Apps
Search
Social
Newsletter
Copyright © 2019 ARCAD INC. All rights reserved.





